Travis CI
The following example shows how to use Turborepo with Travis CI.
For a given root package.json:
And a turbo.json:


Create a file called .travis.yml in your repository with the following contents:
For more information visit the pnpm documentation section on Travis CI integration, view it here
Remote Caching
To use Remote Caching, retrieve the team and token for the Remote Cache for your provider. In this example, we'll use Vercel Remote Cache:
TURBO_TOKEN- The Bearer token to access the Remote CacheTURBO_TEAM- The slug of the Vercel team to share the artifacts with
To use Vercel Remote Caching, you can get the value of these variables in a few steps:
- Create a Scoped Access Token to your account in the Vercel Dashboard
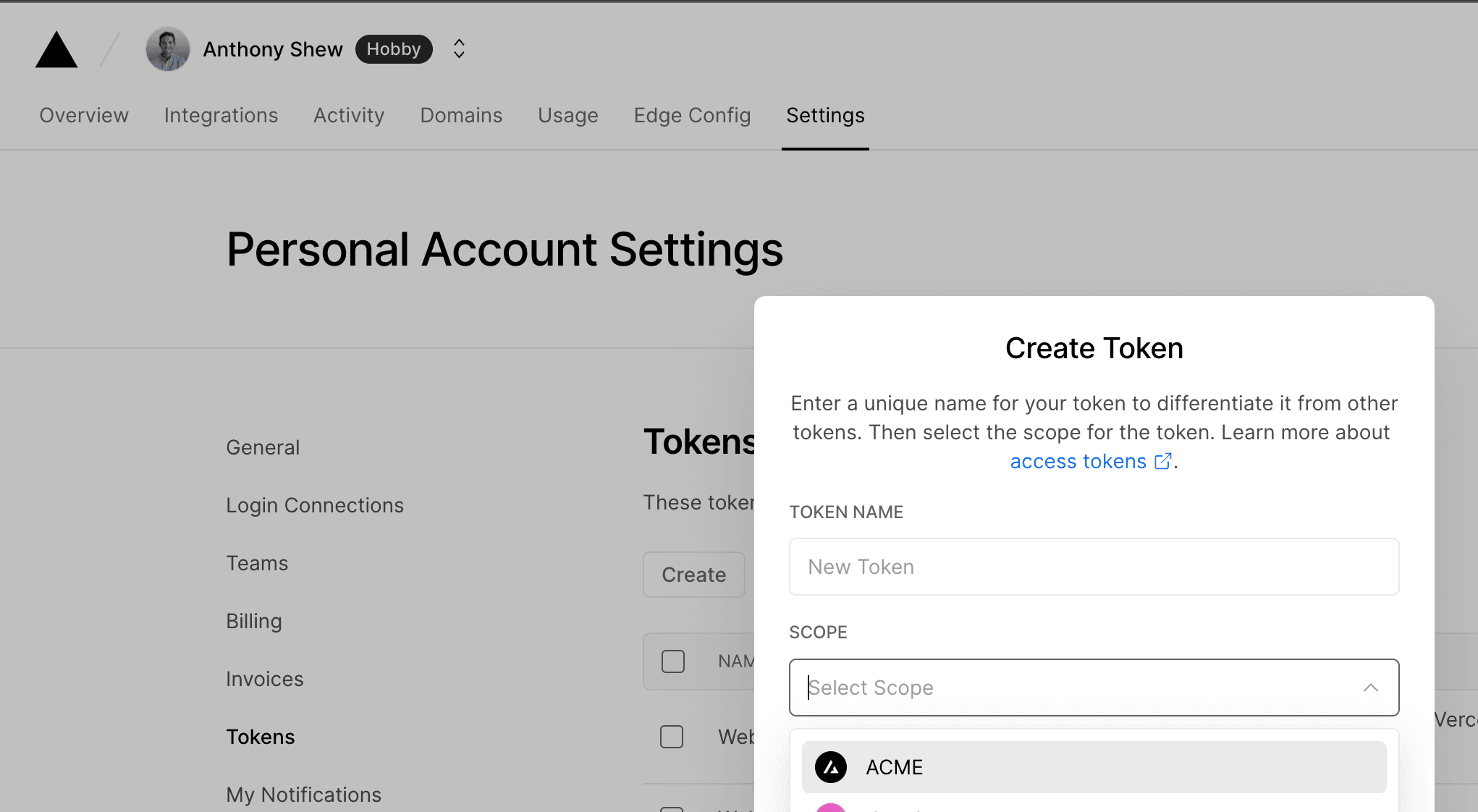
Copy the value to a safe place. You'll need it in a moment.
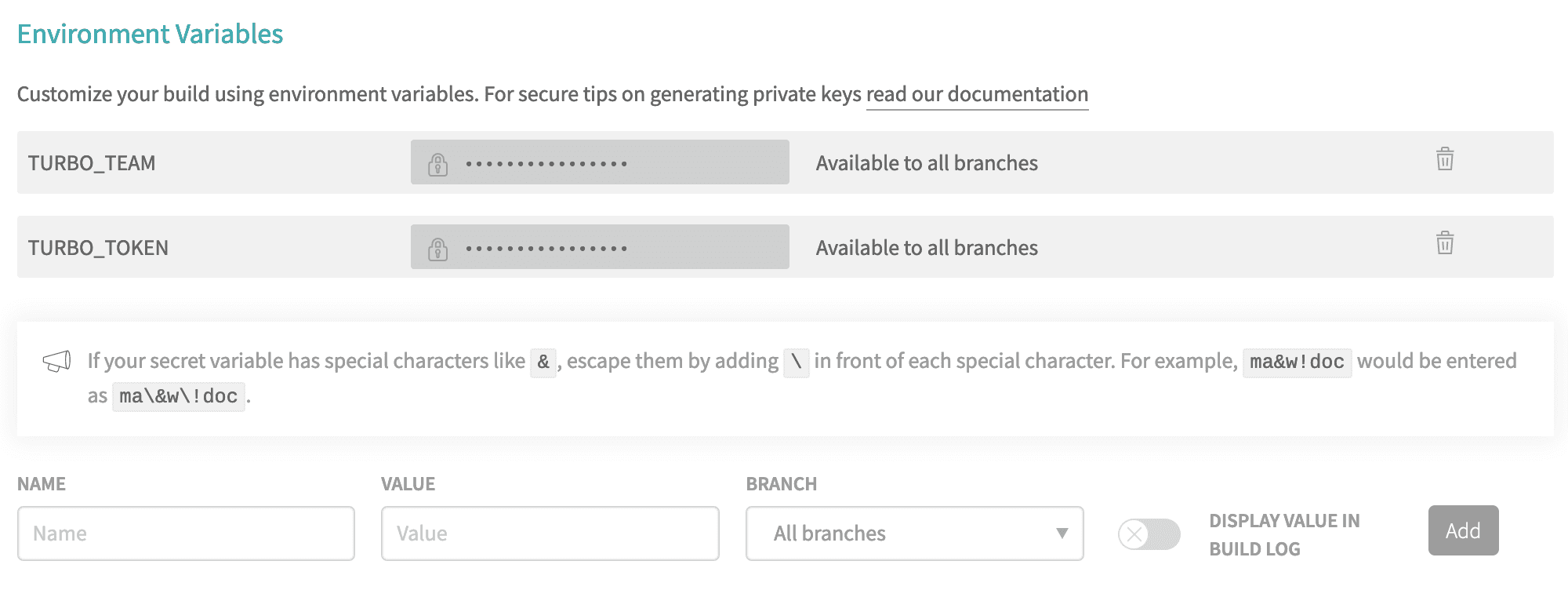
- Go to your Travis repository settings and scroll down to the Environment Variables section. Create a new variable called
TURBO_TOKENand enter the value of your Scoped Access Token.
-
Make a second secret called
TURBO_TEAMand set it to your team slug - the part aftervercel.com/in your Team URL. For example, the slug forvercel.com/acmeisacme. -
Travis CI automatically loads environment variables stored in project settings into the CI environment. No modifications are necessary for the CI file.